To many poor people, jiggers are a big problem that has affected their health and daily life. Despite this, the government has been reluctant to address this issue. Both children and adults are the victim of this problem.
An estimated 1.4 million Kenyans suffer from jigger infestation in the country. Tungiasis is a disease of the poor and poor hygiene is one of the major causes of infestation. Children from impoverished communities and families in the country who are affected are not able to walk properly and thus miss out on school. In adults, the inability to use the limbs affected due to pain in the affected areas hampers normal economically productive activities. The stigma associated with the disease has a debilitating psychological effect on the affected. Secondary infection due to the wounds caused by the jiggers may cause life-threatening complications such as tetanus or gangrene.
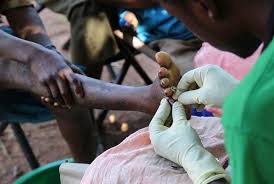
Effective Non-invasive Treatment of Jiggers
Use of potassium permanganate (antiseptic) and petroleum jelly is the most effective non-invasive way of treating jigger infestations. This treatment has been demonstrated to eradicate the jiggers, enabling affected children and adults to return to work or school. The treatment is quick, effective, and painless. It is important not to use sharp objects to remove jiggers since this results to open wounds.
Treatment procedure
- Clean the area by soaking in a basin filled with soap and water
- Add potassium permanganate to the basin and soak for 10-15 minutes
- Dry the feet and hands
- Generously apply Vaseline to the area
- Remove gloves and wash hands

